A. A. Karasev, S. V. Aleshin
Recommendations on SCENAR and COSMODIC treatment
Basic terms pertaining to SCENAR-therapy
Dynamics of body reactions is determined by the following skin characteristics:
- primary characteristics — small skin areas differing from the rest skin integument and available before treatment (colour, itch, pain, injuries, erosions, nevus pigmentosus, trophic disorders);
- secondary characteristics — differences appearing outside the acted upon area while treating (hyperemia or pallor, itch, focal pain or any other actual complaint, localization of the pain focus after treatment, skin moistness (perspiration));
- asymmetry (small asymmetry) — local (only in the area of action) change appeared during the process of treatment or resulted from it. These changes are: skin moistness, skin colour, sensations of the patient (painful or insensitive area), sound while moving the electrode on skin, and “sticking” of the electrode.
- “Sticking” of the electrode — is a subjective sensation due to the electrode being moved with some difficulties on the skin surface because of its moist condition.
- Horizontal — is areas placed on the same horizontal line.
- Segment — is areas placed on the same innervation segment.
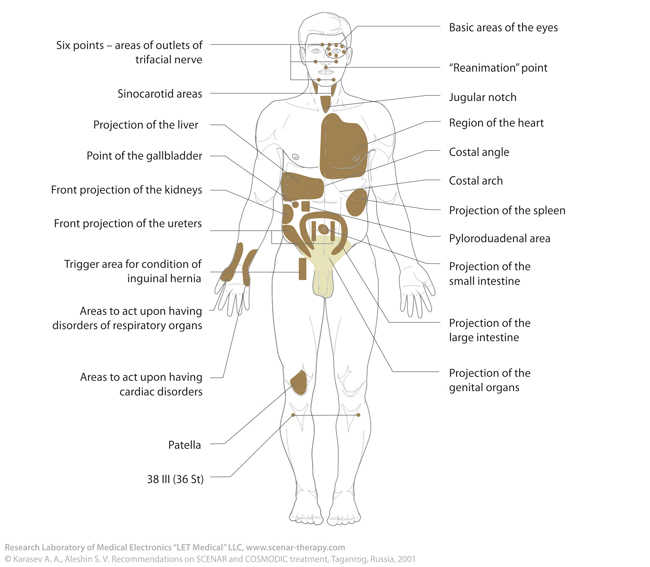
There are basic areas for action (obligatory for treatment, regardless of the form of pathology, excluding cases requiring action upon certain areas, such as strain, injuries, fractures, bruise and the like):
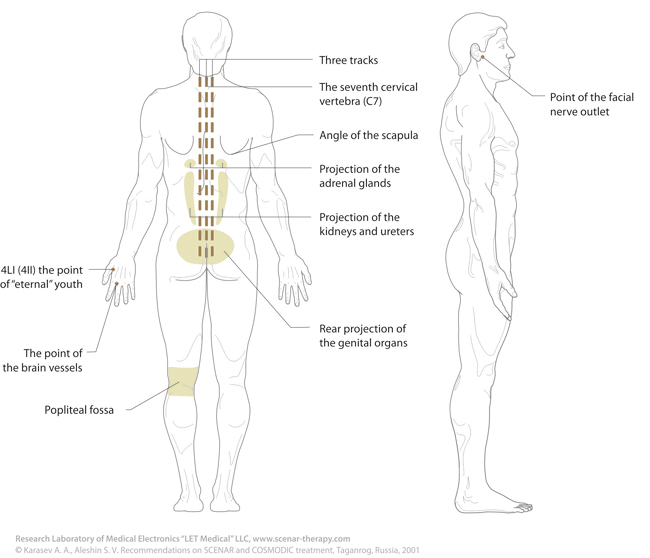
- three tracks — the areas of vertebral column along the spinous processes and two paravertebral lines at the distance of the electrode width from the vertebral column;
- six points — areas of outlets of trifacial nerve, in three on each side of the face;
- 4LI (4II) — the point of “eternal” youth, basic regulating point on the dorsal surface of the palm between thumb and forefinger;
- collar area — cervicobrachial region;
- front and rear projection of female genitals.
- Small areas — rear projection of adrenal glands, the seventh cervical vertebra, jugular fossa, and scrotum.
- Symmetric area — area located at the same distance across the vertebral column.
- Direction vector — the effect of treatment depends upon the direction of the electrode posing and moving.
- Trigger area — is the area that provides maximum response reaction of the body upon the action.
- “Herring-bone” pattern — movements bottom-up along the bronchi.
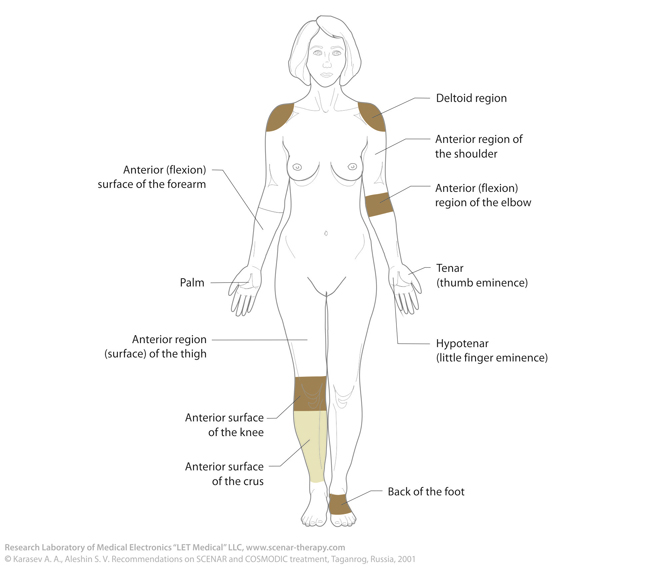
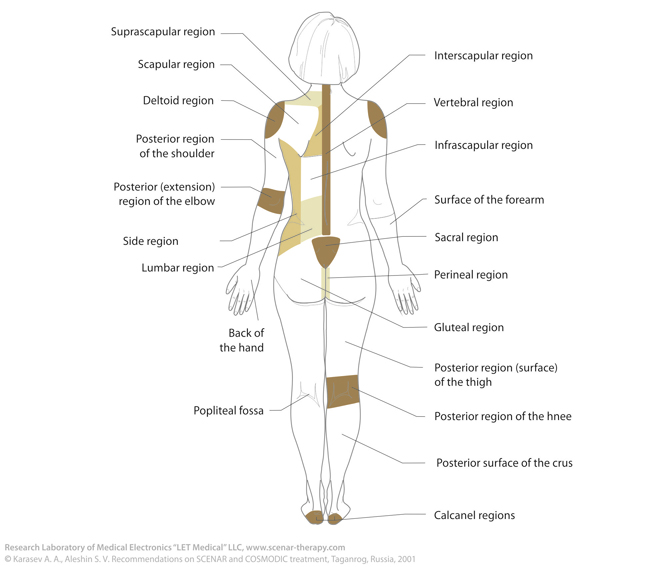
Every day SCENAR-therapist has to deal with the names of the areas for treatment. That is why, we provide you with anatomic notions for body areas and a number of conventional lines, which will help you in determining exact body regions for action.
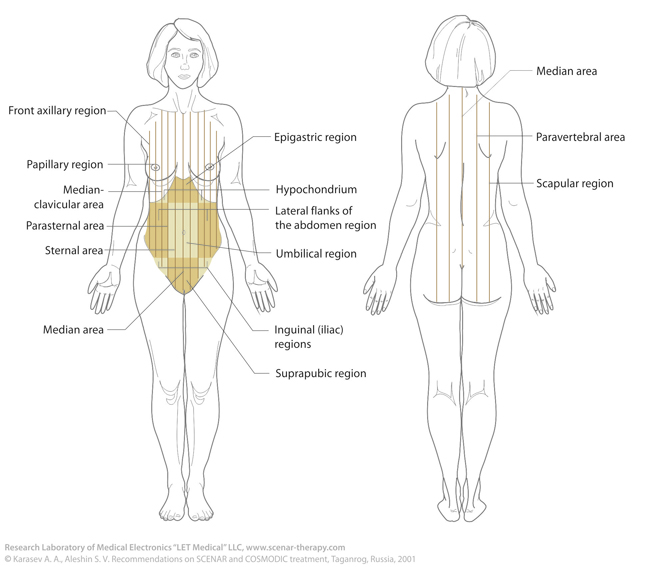
Vertical lines
| Name |
Location |
Anteromedian
Posterior vertebral |
Along the center of sternum, from jugular notch to the middle of pubis.
Along the spinous processes of vertebrae |
Sternal right, left
Median-clavicular right, left
Parasternal right, left
Papillary right, left |
Along the edges of sternum
Across the middle of clavicle
In the middle between sternal and median-clavicular lines
Individually for every patient — along the papillae, often between median-clavicular and axillary anterior lines, but closer to median-clavicular. |
Axillary anterior
median
posterior |
Along the anterior edge of axilla.
In the middle of axilla.
Along the posterior edge of axilla. |
Scapular
Paravertebral |
Across the lower angle of scapula, in position with arms down.
In the middle between vertebral and scapular lines. |
Horizontal lines
| Name |
Location |
Costal
Iliac |
Connects lower ends of costal arches
Connects spinae iliaca anterior superior |
Correlation of the internal organs with segments of cutaneous innervation (scheme of hyperalgesia areas in cases of internal disease)
| Organ |
Side |
Segments of cutaneous innervation |
| According to Zakharjin — Head |
Others |
Lungs, bronchi,
Pleura |
left/right
left/right |
С3 С4 D2 …D5 |
С3 С4 D3 …D9
С3 С4 (D2) D3 …D10 (D11 D12) |
| Heart, pericardium |
left>right |
С3 С5 D1 …D8 |
С3 С4 С8 …D8 |
| Esophagus |
|
D5 D6 …D8 |
С3 С4 D5 D6 |
| Stomach |
left>right |
D7 …D9 |
С3 С4 D5 …D9 |
| Duodenum |
right |
D6…D10 |
С3 С4 Д6 …Д10 |
Small intestine
Ileum |
left
right |
D9 …D12 |
С3 С4 D8 …D11
С3 С4 (D8 D9) D10 D11 |
Large intestine
Blind gut
Appendix
Colon
ascending
transverse (prox.)
transverse (dist)
descending
sigmoid
Rectum
|
right
right
right |
D9 …D12
|
С3 С4 D9 …D12
С3 С4 (D9)D10 …L1
С3 С4 (D9 D10) D11 …L1 |
| Pancreas |
left |
D7 …D9 |
С3 С4 D7 …D9 |
| Spleen |
left |
D7 …D9 |
С3 С4 D7 D8 D9 (D10) |
Liver,
gallbladder |
right |
С3 С4 D8 …D10
D 5…D7 D8…D9 |
С3 С4 D6 …D10 |
Kidneys, ureter,
urinary bladder,
urethra |
left right
left right
right/left
|
D10 D11 D12 L1
D11 D12 L1
D11 D12 L1 S3 S4 |
С3 С4 D9 …D11 (L1 L2)
С3 С4 D9…L2 (L3) |
| Peritoneum parietale |
|
|
С3 С4 D5 …D12 |
Adrenal glands
Mammary glands
|
left right
left right |
D7 D8
D4 D5 |
|
Genitals
Ovary, testes, prostateа
Uterine tube
neck of the uterus
body of the womb
|
left right |
D10
D10 D11 S1…S3 S5
D11 D12
D11 D12 S1…S4
D10 L1
|
С3 С4 D5 …D12 |
| Region of head |
Corresponding internal organs |
| Frontonasal |
Apices pulmonis, stomach, liver, aortic ostium, C3 C4 |
| Median-orbital |
Lungs, heart, ascending aorta, D2 …D4 |
| Frontotemporal |
Lungs, heart, D5 D6 |
| Temporal |
Lower lobes of the lungs, heart, cardial part of the stomach, D7 |
| Parietal |
Pylorus, upper part of the intestine, D9 |
| Occipital |
Liver, large intestine, ovaries, testes, uterine tubes, uterus, urinary bladder, D10 …D12 |
|





